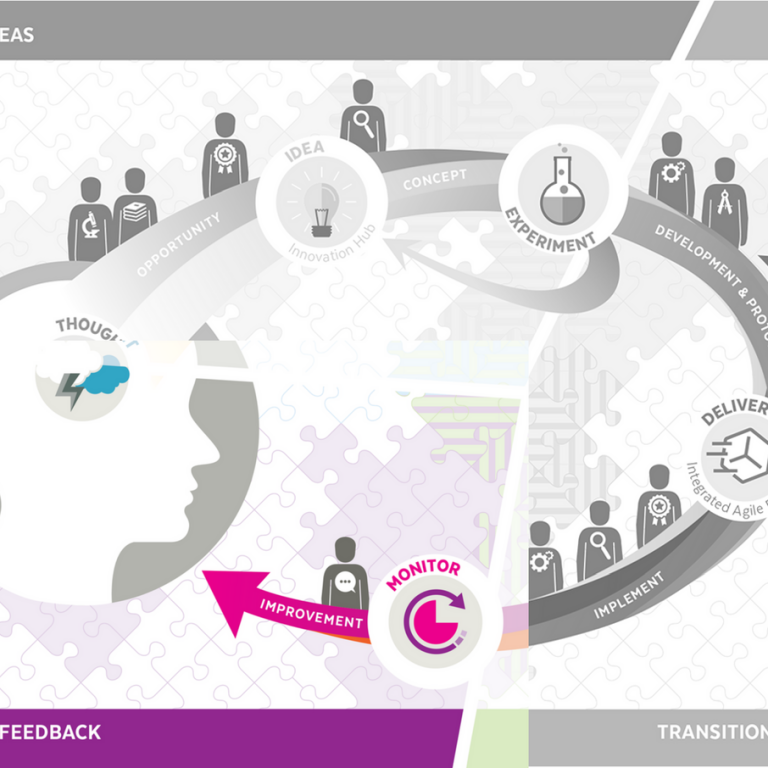
 In the Monitor and Feedback phase you are observing and managing the output from the Transition to Reality phase utilising best practice and knowledge management, thus furthering innovation results. This phase provides a competitive advantage for the organisation as the output simultaneously provides feedback on potential process improvement and capability transformation. This is a useful input for key stakeholders when the phase transitions back into Incubate Ideas.
In the Monitor and Feedback phase you are observing and managing the output from the Transition to Reality phase utilising best practice and knowledge management, thus furthering innovation results. This phase provides a competitive advantage for the organisation as the output simultaneously provides feedback on potential process improvement and capability transformation. This is a useful input for key stakeholders when the phase transitions back into Incubate Ideas.This phase also sets up the foundation for innovation-as-a-culture for the organisation. Oftentimes, the best ideas come from the janitor who’s been there for years, not the thousand-dollar consultants you hire off the street.
Establish the CoE of MBT
In recent years, many organisations have increased their efforts in the development of innovative products. However, the products struggle to maintain existence and preserve their competitive advantage – both in terms of long-term presence and for triggering more innovation. This is due to a lack of understanding of the importance of maintaining innovative product uniqueness in terms of competency and capability.
MBT addresses these issues by integrating the Value-Chain process from the Transition to Reality phase through establishment of the Centre of Excellence (CoE) unit within the organisation. This ensures that organisational knowledge and its uniqueness can be retained as best practice. The unit can also help the organisation to facilitate specific innovation training and become a research-and-development (R&D) unit for revitalising stalled initiatives.
Some of the capabilities include:
- Strategy and Process Capability Linkage
- Knowledge Management
- Education and Learning
- Collaboration and Communication
- Value and Benefits
- CoE and Social Networks
Establish DevOps Practices for Change
Nowadays, each organisation needs to standardise their process and follow the best practice and global standard for their ICT process to cope with continuing changes.
Many organisations have been putting a lot of investment so that better collaboration and communication between their software development and software delivery and infrastructure changes process.
DevOps has been extensively used as the new norm to address this, but how effectively can this practice respond to the challenge of keeping up with disruptive changes within an innovation environment?
MBT aims at establishing a culture and environment where building, testing and releasing software happens rapidly, frequently, and more reliably. This is combined with the Agile concept and pre-configured tools ensure that any change can be addressed quickly and adapted easily.
Some of the capabilities including:
- Business Architecture
- Process Metrics and Performance Linkage
- Process Management Standards
- Process Management Controls
- Improvement Design and Execution
- Project & Program Maintenance
- System Design and Modelling
- Tool Implementation & Execution
- System Tool and Control Measurement
- Technology Transformation
- Skills and Expertise
- Education and Learning
- Collaboration and Communication
- Centre of Excellence (CoE) and Social Networks
Establish a Continuous Change Culture
Building a continuous change culture is not just about executing a handful of process improvement or innovation projects. (That’s a good place to start – and companies may reap tangible rewards from those projects.) More is required to drive sustainable results over time and embed continuous improvement into the very fabric of the organisation. That’s when the kind of real, transformational changes take place that can generate hundreds of millions of dollars of opportunities.
MBT provides the material to establish this culture within the organisation by introducing the cycle of Thought-to-Reality as part of continuous learning and development throughout the process. This means that the process doesn’t stop when the viable product has been released to the market but continues long term so the organization is more innovative, resilient and ready for changes. Ultimately transforming into a continuous change culture across the organisation.
Some of the capabilities include:
- Stakeholder Management
- Knowledge Management
- Education and Learning
- Collaboration and Community
- Accountability
- Responsiveness and Change
- Value and Benefits
- Attitudes and Behaviours
- Leadership Attention to Transformation and Innovation
Capabilities to Notice in this Phase
Strategy
-
Transformation Plan
-
Strategy and Process Capability Linkage
-
Business Architecture
-
Innovation Plan
-
Stakeholder engagement
-
Process
-
Process Management Decision Making
-
Process Roles and Responsibilities
-
Process Metrics and Performance Linkage
-
Process Management Standards
-
Process Management Controls
-
Methods
-
Improvement Design and Execution
-
Transformation Design and Execution
-
Innovation Design and Execution
-
Governance, Control and Measurement
-
Project and Program Management
-
Technology
-
System Design and Modelling
-
Tool Implementation and Execution
-
System and Tool Control and Measurement
-
Technology Transformation
-
Project and Program Implementation
-
People
-
Skills and Expertise
-
Knowledge Management
-
Education and Learning
-
Collaboration and Communication
-
Accountability
-
Culture
-
Responsiveness and Change
-
Values and Beliefs
-
Attitudes and Behaviours
-
Leadership Attention to Transformation and Innovation
-
Centre of Excellence (CoE) and Social Network
-
